Side Effects
Does Semaglutide Cause Constipation and What Can You Do About It?

Weight loss can come with unexpected challenges, and digestive discomfort is one of them. Many using Semaglutide (Ozempic) for weight management find themselves asking, “Does Semaglutide cause constipation?.” Understanding how this medication affects digestion is key to staying on track with your health goals.
To support your progress, our GLP-1 app helps manage your health while taking Semaglutide by tracking key metrics and offering insights that keep you organized and motivated.
Summary
Semaglutide commonly slows gastric emptying, which makes constipation a predictable pharmacologic effect, with 15% of clinical trial participants reporting constipation as a side effect.
Real-world data show that about 20% of people taking semaglutide report constipation, indicating a substantial minority encounter this issue in routine use.
Clinically significant constipation is defined as fewer than three bowel movements per week, and semaglutide-related changes typically present as reduced frequency, hard, dry stools, or abdominal bloating.
Constipation often appears as part of a gastrointestinal symptom cluster, including nausea, early satiety, and gas. Those interactions can reduce fiber and fluid intake, and over 4 to 8 weeks of tracking, this was the usual trigger that turned mild slowing into troublesome constipation.
Early, modest habit changes such as increasing plain fluids and gradual soluble fiber often resolve symptoms, but if constipation persists beyond about 2 weeks or is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid abdominal swelling, or inability to pass gas, contact your clinician promptly.
Memory-based symptom reporting masks timing correlations and delays adjustments, while time-stamped logging and trend visualization can compress weeks of guesswork into clinician-ready evidence, which matters given that 10% of patients using semaglutide for weight loss reported constipation in some sources.
This is where MeAgain's GLP-1 app fits in: it centralizes time-stamped dose and symptom logging, automates hydration and fiber reminders, and visualizes when constipation aligns with doses or dietary changes.
Table of Contents
Why Does Semaglutide Cause Constipation?

Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. This means that it helps activate the GLP-1 receptor and performs some of the actions of GLP-1, a hormone involved in a number of digestive processes that occur after eating. This includes regulating how much insulin the body produces, which helps maintain lower blood sugar levels and prevents hyperglycemia in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Part of this process also involves slowing down how quickly food moves through the digestive tract. This results in slower stomach emptying and reduced muscle contractions in the intestines, which can cause stool to back up in the colon. As stool builds up, it can dry out and form blockages—ultimately leading to constipation.
For those experiencing digestive discomfort, the guide on Tummy problems on GLP‑1 offers helpful strategies.
How Long Does Ozempic Induced Constipation Last?
Ozempic-related constipation can last about 6 weeks, or 47 days, according to one study. This study showed constipation went away on its own as the body adjusted to Ozempic.
There is limited research on this topic, so individual experiences may vary. Some people may feel better sooner, while others may take longer to experience relief.
Higher doses of Ozempic have been linked to increased frequency of constipation. This means symptoms may return if a higher dose is prescribed.
For more on adjusting treatment plans, see Getting a GLP‑1 Prescription.
Why Does Ozempic Cause Constipation?
Ozempic causes constipation due to how it affects the digestive system.
Ozempic slows down how fast the stomach empties. This makes people feel fuller for longer, leading to reduced food and fluid intake. Not drinking enough fluid can cause stool to harden, making it more difficult to pass.
Not consuming enough fiber is a major factor in constipation. Fiber adds bulk to stool, making it easier to move through the digestive tract. Since people often eat less overall while taking Ozempic, they might also consume less fiber.
In addition, fiber can worsen other Ozempic-related side effects such as nausea, gassiness, and bloating. As a result, individuals may be more likely to avoid fiber, further contributing to constipation.
Together, these effects can result in hard, infrequent, and uncomfortable stools. Although bothersome, this side effect can often be alleviated through lifestyle changes.
Tips for Managing Constipation
The following tips can help manage constipation while taking semaglutide, making it easier to enjoy the benefits of the medication with less discomfort:
Increase your daily fluid intake to help soften stool and promote regular bowel movements.
Include more high-fiber foods in your meals or use supplements if needed, while monitoring tolerance to avoid exacerbating nausea or bloating.
Incorporate gentle physical activity, like walking, to help stimulate digestion.
Talk to a healthcare provider about over-the-counter remedies or prescription options if symptoms persist.
A Supportive Tool for Your GLP-1 Journey
MeAgain offers a playful, goal-oriented approach to tracking health metrics like protein, fiber, water, and exercise. Its adorable capybara mascot helps users stay consistent with daily health habits.
With features like the Journey Card, users can capture milestones and stay motivated during rapid health transformations. As the only all-in-one GLP-1 app, MeAgain turns the process into a rewarding experience.
Related Reading
How Do You Prevent Constipation on Semaglutide? 10 Expert Tips to Prevent Constipation while taking Semaglutide

1. Drink Up to Keep Things Moving
Hydration is key for keeping your digestive system in good working order. When you’re constipated, drinking more water can help relieve your symptoms. Dehydration can make your digestive system sluggish, leading to harder stools that are difficult to pass. Staying well-hydrated is especially important when you’re using semaglutide, which can cause dehydration.
Aim for at least eight to ten 8-ounce glasses of water daily, or even more if you’re active. If you find it challenging to drink enough water, try carrying a reusable bottle with you and setting reminders on your phone.
Herbal teas, like peppermint or ginger, and water-rich foods, like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges, can also help you stay hydrated and support your digestion. You can find hydration tips in our Hydration on GLP‑1 article.
2. Increase Your Fiber Intake Gradually
Increasing your fiber intake can help you manage or prevent constipation while using semaglutide. Fiber plays a critical role in relieving constipation by adding bulk to your stool, making it easier to pass.
However, introducing too much fiber too quickly can cause bloating and worsen digestive distress. To avoid this, gradually increase your fiber intake over a week or two, allowing your body to adjust.
Focus on including fiber-rich foods like whole grains, leafy greens, beans, and fresh fruits. Insoluble fiber, found in foods like whole grains and certain vegetables, helps bulk up stools, while soluble fiber in oats and fruits absorbs water and softens stools.
Aim for a total fiber intake of 25 to 30 grams daily, but start slowly if you’re not used to high-fiber diets. See more on GLP‑1 Medication overview.
3. Eat More Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics support gut health to alleviate constipation. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
On the other hand, prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed these bacteria, and are found in foods like bananas, onions, and garlic.
Adding both to your diet can improve digestion and help maintain regular bowel movements. If you’re new to probiotics, consider starting with a small amount, as a sudden increase may initially cause gas or bloating.
You can also consider a probiotic supplement, but consult your healthcare provider before beginning any supplement. Our post on Mindset & Mood on a GLP‑1 includes more wellness guidance.
4. Get Moving
Exercise can be a simple yet effective remedy for constipation. It stimulates the muscles in your intestines, helping to move stool through your digestive tract.
Even a daily 20-to-30-minute walk can significantly improve your digestion and relieve constipation. For a balanced approach, engage in a mix of aerobic exercises, like walking or cycling, and strength training.
To encourage digestion, try incorporating gentle exercises, like yoga or stretching, especially after meals. You don’t need to embark on a rigorous workout regimen; even light movements can make a noticeable difference in how your body processes food.
Learn more in Workouts & Recovery on GLP‑1.
5. Skip the Junk Food
While it can be tempting to indulge in convenient, processed foods, they’re often high in unhealthy fats and low in fiber, which can exacerbate constipation. Foods like fried items, processed snacks, and sugary treats can slow digestion and worsen constipation.
Limit these foods while on semaglutide and replace them with whole, natural foods that support digestion. Consider swapping fast food for homemade meals that contain lean proteins, whole grains, and a variety of vegetables.
Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes, reducing your intake of fats that may interfere with digestion. Visit our Blog for more healthy food swaps.
6. Stool Softeners Can Help
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough to relieve your constipation, consider using stool softeners or mild laxatives under medical supervision. Stool softeners add moisture to your stool, making it easier to pass, while gentle laxatives stimulate bowel movements. However, these products should only be used briefly to avoid dependency or disruptions to your natural bowel patterns. You can also review our tips for GLP-1 injection management.
7. Know Your Over-the-Counter Options
OTC laxatives and stool softeners can offer quick, affordable relief from constipation. However, OTC laxatives aren’t for long-term use. Your body can become dependent on these medications, which can cause chronic constipation. You should stop taking the laxatives as soon as you have a bowel movement, and avoid taking laxatives for more than a week at a time. Options for short-term OTC laxatives and stool softeners include:
Bisacodyl (Dulcolax): Bisacodyl is a laxative that stimulates the muscles in your intestines to help you pass bowel movements.
Docusate: Docusate helps water penetrate and mix into the stool by reducing surface tension making it easier to pass.
Magnesium hydroxide (Phillips’ Milk of Magnesia): Magnesium hydroxide is a laxative that works by helping your intestines retain more water, which in turn softens your stools.
Polyethylene glycol (Miralax): This laxative helps absorb water into your stool, which softens it and makes it easier to pass.
Sennosides (Senna): Sennosides are a type of laxative that stimulate the nerve endings in your colon muscles, causing them to contract and help push stool through your colon. See our guide to Types of GLP‑1 Drugs & Brands for more.
8. Mindful Eating Matters
Eating mindfully and slowly can help improve digestion, making it easier for your body to process food and absorb nutrients. Eating too quickly makes you more likely to swallow air, which can lead to gas and bloating, further contributing to constipation. Try to eat in a relaxed environment, focusing on each bite, and take the time to chew your food thoroughly.
Mindful eating also means paying attention to portion sizes. Overeating can lead to discomfort and digestive issues, so listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid overloading your digestive system and maintain comfort.
Read more in Substances & socializing on glp1.
9. Take It Slow
A doctor may recommend you start by taking semaglutide at a low dose to know whether you’ll have any serious side effects.
If you don’t have constipation while taking a low dose, your doctor will start gradually increasing your dose over a few weeks. If you start having constipation at higher doses, reduce your dose again. Find support in our Maximising GLP‑1 Results.
10. Talk With Your Doctor
It’s also a good idea to talk with your healthcare team if you’re experiencing constipation while taking Ozempic. They might be able to adjust your dosage, so you don’t have trouble going to the bathroom. It’s also possible that other medications you’re taking could be contributing to constipation.
Don’t stop taking any of your medications without talking with a healthcare professional. They might adjust these medications or swap them out for something else. Also, check out our article on GLP‑1 Medication overview to better understand how your treatment works.
Related Reading
Common Symptoms of Semaglutide Constipation
Yes. Constipation is a known side effect of semaglutide because the drug slows the rate at which food moves through the stomach and intestines, which can reduce stool frequency and change stool consistency. Those effects manifest differently from person to person, so watch for specific, observable signs rather than assuming severity from the label alone.
Why Does Semaglutide Slow Digestion?
Semaglutide acts on GLP-1 receptors that regulate appetite and gut motility; therefore, slowed gastric emptying and intestinal transit are predictable pharmacologic effects. Think of it like a traffic jam in your digestive tract: food and waste move more slowly, vehicles back up, and the road feels tighter. Slowed transit underlies the symptoms reported and explains why gastrointestinal effects are among the most common during dose adjustments.
How Common is this for People Taking Semaglutide?
Approximately 20% of people taking semaglutide report experiencing constipation, according to Healthline, indicating that a substantial minority encounter this side effect in routine use. In controlled clinical trials, 15% of participants experienced constipation as a side effect of semaglutide according to Healthline, indicating that trial data and real-world reports point to the same signal. However, individual risk varies with dose and timing.
What Does Constipation From Semaglutide Actually Look Like?
Fewer bowel movements. Constipation typically means fewer than three bowel movements a week, so a drop in your normal frequency is the clearest early sign.
Hard, dry stools. Slower transit usually produces firmer, drier stool that can be difficult or uncomfortable to pass.
Bloating or abdominal discomfort. When bowel movements are slow, you may experience fullness, bloating, or a sense of incomplete evacuation even after using the bathroom. These are observable, non-graphic signs that tell you something has shifted in how your gut is working.
Turning Symptom Guesswork into Clear Actionable Signals
Most people manage symptoms by tracking patterns and communicating them to their clinician, but they often rely on memory or sporadic notes. That approach feels familiar and low-effort, but it hides the actual cost: inconsistent reporting, missed timing correlations with dose changes, and delayed adjustments that prolong discomfort.
Solutions like MeAgain that centralize symptom logging, automate timing with your dosing schedule, and visualize trends help people identify which changes align with symptoms, compressing discovery from weeks of guesswork into clear, actionable signals.
How Variable are Symptoms, and When Do They Show Up?
Symptoms can begin soon after you start or increase a dose, or they can emerge later as your body adjusts. Severity ranges from a brief, mild slowdown that resolves in days to a persistent change that requires clinician review:
Personal history
Hydration
Diet patterns
Other medications
All shape the course. Trackable, time-stamped entries are the only reliable way to distinguish random fluctuations from patterns worth addressing.
That seems straightforward, but the ways constipation links with other semaglutide side effects are more complex and more revealing than most people expect.
What Other Side Effects of Semaglutide relate to Constipation?
Yes. Constipation often shows up alongside other gastrointestinal symptoms like:
Nausea
Reduced appetite
Abdominal fullness
Gas
General stomach discomfort
These symptoms can amplify one another, so constipation feels worse than an isolated bowel change. Not everyone will experience all of these effects, and for many people, the pattern shifts over days to weeks as your body adapts or as doses change.
What Other GI Symptoms Should You Watch For?
Nausea and early satiety are common, as are bloating, increased gas, and intermittent stomach cramps. These symptoms are not separate little problems; they form a cluster.
For example, nausea can lead you to eat smaller, more bland meals, which reduce fiber and fluid intake, and that dietary change directly increases the risk of harder, drier stools. Feeling full after small meals also changes with what and when you drink, so hydration dips precisely when your colon needs water to keep stool soft.
How Do These Symptoms Interact With Constipation?
Think of your gut as a production line.
Slower movement is the conveyor problem, and nausea, low appetite, and bloating remove the lubricant and packaging materials.
Reduced intake of fiber and fluids shrinks stool volume and raises water reabsorption in the colon, making stool firmer.
Gas and cramping make people avoid the bathroom or tighten pelvic muscles, which makes evacuation more difficult.
The result is a feedback loop:
One symptom feeds into another until you intentionally break the cycle.
When Should You Change Habits, and When Should You Seek Help?
Small, early interventions usually work:
Increase plain fluids
Add a modest
Consistent fiber source
Favor softer
Wetter foods
Those are easier to pass. If symptoms persist beyond a couple of weeks despite modest changes, or if you develop severe, worsening abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid abdominal swelling, or inability to pass gas, call your clinician right away because those signs suggest a blockage or other serious complication. Keep timed notes so you and your clinician can see whether symptoms track with dose increases, meal timing, or other medications.
Practical, Personalized Steps that Make a Real Difference
Hydration first, but practical: Drink a glass of water on waking and another 20–30 minutes after meals to create predictable hydration moments, not vague goals.
Fiber with structure: Aim for gradual increases, favoring soluble fiber sources such as oats, psyllium, or beans that bulk stool without causing excessive gas. Add fiber over one to two weeks to allow the gut to adapt.
Rethink meal timing and texture: Smaller, more frequent meals with higher water content, such as soups or smoothies with protein, preserve calories while reducing the chance of low-fiber, dry meals.
Use gentle aids when needed: Stool softeners or osmotic agents taken intermittently can ease transitions, but treat them as tactical, time-limited tools and coordinate with your clinician.
Log what matters: Time of dose, meal size and type, fluid intake, and stool quality, not vague impressions.
When Habit-Based Answers Fail, The Signal is in the Pattern
After working with participants for four to eight weeks who tracked GLP-1 use and symptoms, the pattern became clear: appetite loss commonly produces a sustained reduction in fiber and fluid intake, and that dietary shift is the usual trigger that turns moderate slowing into troublesome constipation. Tracking distinguishes between guessing and acting on evidence.
Turning Symptom Noise Into Actionable Data
The familiar way most people manage these side effects is ad hoc, using memory and mismatched notes that create noise, not answers. That approach works for occasional discomfort, but as symptoms persist, it obscures causal signals and delays more informed decisions.
Solutions like MeAgain centralize time-stamped symptom logging, automate reminders for hydration and fiber windows, and visualize when dose changes line up with GI shifts, turning fuzzy recollection into precise, clinician-ready data that shortens the path to effective adjustments.
Navigating Side Effects and Real World Results
A final practical caution, and an evidence note to keep perspective: constipation was reported by 10% of patients using semaglutide for weight loss, according to Healthline, which helps explain why routine monitoring matters when you start or increase the dose.
Also, real-world experience and trial data differ slightly, reflecting how everyday habits can amplify or reduce risk, as shown by approximately 20% of people taking semaglutide who report constipation in some sources.
That sounds like an ending, but there is one more question people always press for that changes how you act next.
Remove the highlighted subsection above. In its place, paste the new content/section above the section highlighted above.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does Constipation on Ozempic® Go Away?
Constipation on Ozempic® should go away. Most people experience constipation during the first 16 weeks of taking a GLP-1 drug that’s a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, like Ozempic®. Constipation should go away with time, though.
FYI, Ozempic® is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to help people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. But it’s sometimes prescribed off-label for obesity and weight loss.
When Should I See a Doctor About Semaglutide Constipation?
You should see a medical professional if your semaglutide constipation doesn’t improve after trying lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments or if constipation becomes severe.
A healthcare provider can recommend the best treatments to relieve constipation or adjust your semaglutide dose if needed.
How Can I Relieve Constipation on Wegovy®?
You can relieve constipation on Wegovy® by:
Drinking plenty of water
Eating enough fiber
Doing more exercise
Going to the bathroom at regular times
Taking fiber supplements, stool softeners, or laxatives
Taking prescription constipation medication
Reach out to a healthcare professional if Wegovy® constipation is severe or doesn’t improve.
Can Ozempic or Wegovy Cause a Bowel Blockage?
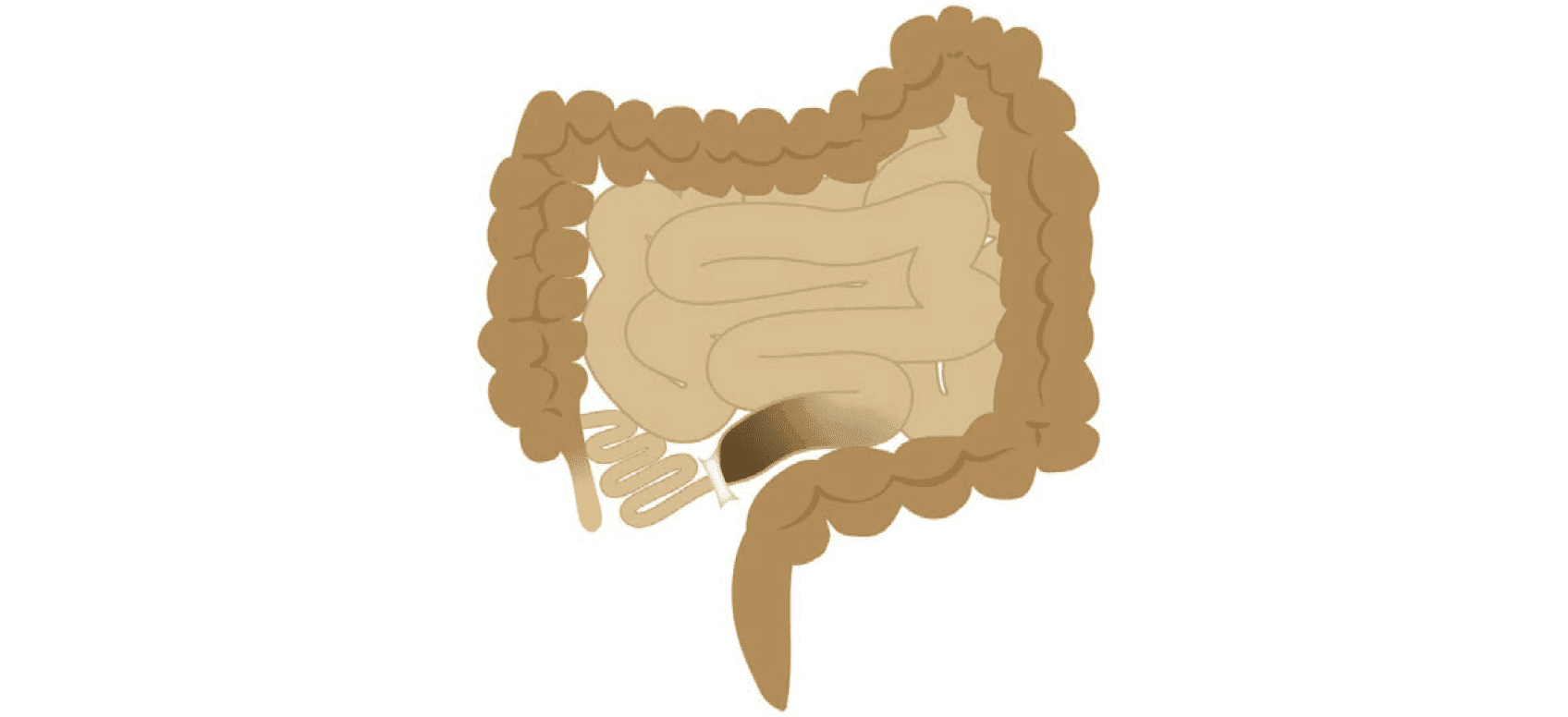
Long-term constipation caused by Ozemic or Wegovy can result in a bowel blockage. In 2023, the FDA updated its labeling for semaglutide to include intestinal obstruction as a possible complication.
Can You Take Laxatives While on Semaglutide?
Yes, you can take laxatives while on semaglutide. It’s always a good idea to run new medications (prescription or OTC) by your healthcare provider. Also, let your provider know if OTC treatments or lifestyle changes aren’t helping with your constipation. You may need a dose adjustment of your semaglutide or a different weight-management strategy.
What Simple Trick Empties Your Bowels Immediately?
There is no simple trick to empty your bowels immediately. But taking OTC laxative stimulants can help you have a bowel movement in a few hours, though you shouldn’t resort to stimulant laxatives regularly. You can also try getting into a better position for pooping, elevating the feet on a footstool to put your legs into a squatting position. This can help reduce straining.
How Do You Prevent Constipation on Semaglutide?
You can reduce your risk of constipation with semaglutide by staying hydrated, eating fiber-rich foods, and exercising regularly.
How Common is Constipation With Semaglutide?
A noticeable portion of users reports constipation, but not everyone experiences it. Some people have mild symptoms, while others may not notice any change at all.
When Does Constipation Usually Start After Taking Semaglutide?
It often appears during the first few weeks of treatment or after a dose increase, when the body is still adjusting to the medication.
Are There Other Semaglutide Side Effects Linked to Constipation?
Yes. Reduced appetite, nausea, bloating, and a feeling of fullness can occur alongside constipation and may contribute to slower digestion.
Is Constipation From Semaglutide Dangerous?
In most cases, it’s not dangerous, but ongoing or severe symptoms shouldn’t be ignored. Persistent discomfort is a good reason to speak with a healthcare provider.
When Should I Contact a Healthcare Provider?
You should reach out if constipation is severe, long-lasting, painful, or interfering with daily life, or if you’re unsure whether your symptoms are related to semaglutide.
Should I Stop Taking Semaglutide if I’m Constipated?
Do not stop or change your medication without medical guidance. A healthcare provider can help determine the best next steps based on your symptoms.
Download our GLP-1 app to Turn Your Weight Loss Journey into Your Favorite Game

GLP-1 medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro come with side effects, such as constipation and muscle loss. Fortunately, MeAgain can help you avoid these side effects, and even turn the process into a game. Our eponymous app helps you hit your goals for protein, fiber, water, and exercise to keep your body healthy and functioning properly while losing weight with GLP-1s.
Plus, you’ll capture your transformation with our Journey Card so you can remember every milestone on your fast-paced journey. Download MeAgain today and turn your weight loss journey into your favorite game.

